3.2 KiB
3.2 KiB
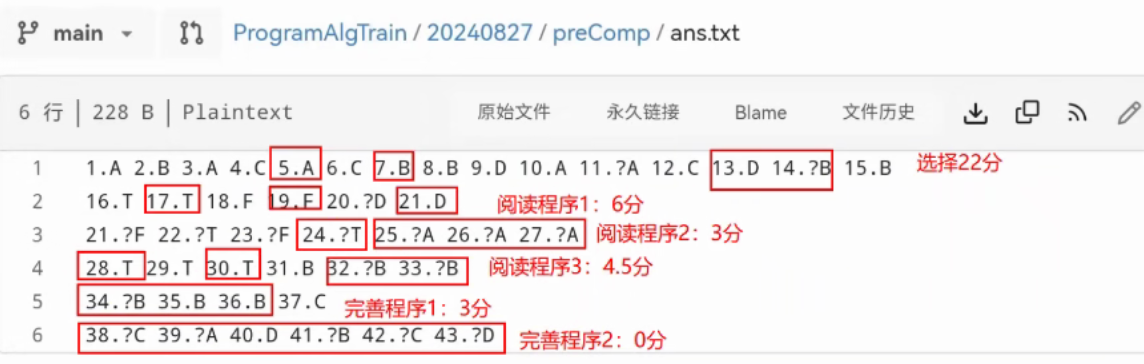
总览
选择
5
算法
n个数组成$Z_{1..n}$,建立数组A_{1..{n\over2}}与B_{1..{n\over2}}
i=[1,{n\over2}],A_i=max(Z_{i},Z_{i+{n\over2}}),B_i=min(Z_i,Z_{i+{n\over2}})
max\_number=A_1,i=[2,{n\over2}],max\_number=\max(max\_number,A_i)
min\_number=B_1,i=[2,{n\over2}],min\_number=\min(min\_number,B_i)
所以总次数是
times={3\over2}n-2
在题目中是2n个数所以是3n-2
7
完全图n个点时
边数={n\times(n-1)\over2}
非连通图+1即可
解方程
{n\times(n-1)\over2}\geq36
最后记得非连通图要+1
答案是10
阅读程序
1
在C++中,cout.flags(ios::fixed) 和 cout.precision() 是用于控制浮点数输出格式的操作。下面分别介绍它们的作用:
1. cout.flags(ios::fixed)
cout.flags(ios::fixed) 用于设置输出流的格式标志,指定以固定小数点记法(即定点格式)输出浮点数。
默认情况下,C++ 会以科学计数法或定点格式输出浮点数,具体取决于浮点数的大小。例如,较大的数字可能会以科学计数法的形式输出,而较小的数字会以定点格式输出。
使用 ios::fixed 作为标志后,所有浮点数都将使用定点格式输出,而不会切换到科学计数法。这意味着浮点数总是以小数点后固定的位数来表示。
示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
double num = 123.456789;
// 默认输出
cout << "默认输出: " << num << endl;
// 设置为定点格式
cout.flags(ios::fixed);
cout << "定点格式输出: " << num << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
默认输出: 123.457
定点格式输出: 123.456789
2. cout.precision()
cout.precision(int n) 用于设置浮点数输出时小数点后的精度(即显示多少位小数)。该函数有两种形式:
- 无参数形式:返回当前的精度设置。
- 有参数形式:设置新的精度并返回之前的精度。
在使用 ios::fixed 标志之后,precision() 函数控制小数点后输出的位数。例如,如果设置了 cout.precision(2),则浮点数将以小数点后两位输出。
示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
double num = 123.456789;
// 设置为定点格式
cout.flags(ios::fixed);
// 设置精度为2
cout.precision(2);
cout << "精度为2的定点格式输出: " << num << endl;
// 设置精度为4
cout.precision(4);
cout << "精度为4的定点格式输出: " << num << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
精度为2的定点格式输出: 123.46
精度为4的定点格式输出: 123.4568
总结
cout.flags(ios::fixed):设置输出浮点数为定点格式(固定小数点)。cout.precision(n):设置浮点数输出的精度,即小数点后显示的位数。
这两个函数常一起使用,控制浮点数的输出格式和精度。
17.
int/int=int
int/double=double
double/double=double
19
//acos的逻辑,逻辑代码
double acos(double num){
find t where{cos(t) == num;}
return t;//弧度制
}